What are Forex Broker commissions? All you need to know!
Table of Contents
The foreign exchange market is the largest in the financial market. Forex brokers and retail traders are among the minor participants in this market. Forex retail traders can not trade the market without a middleman. Brokers act as the middlemen between retail traders and the interbank market. They offer their services for various fees.
These fees constitute trading costs for the trader, so it’s vital that you understand all the commissions you would have to pay while trading. With this understanding, you can do proper research and comparisons before choosing your broker. Below, we explain the different kinds of forex broker commissions and fees so you may know what to expect.

What are forex broker commissions?
Forex broker commissions refer to the fees you pay your broker for their services. The broker may deduct a certain percentage or a specific amount from each trade as the commission.
Forex traders pay different types of fees as they carry out transactions. The commissions are one of the main fees. The broker deducts commission from the Trading account equity whenever you open a trade. So it does not matter whether the trade turns out profitable or not. As soon as you open a trade position, the broker takes the commission for that trade. The amount deducted would depend on the broker and the type of account you’re working with.
Commission rates vary between brokers and the type of account. This is fee is different from the spreads. The difference between ASK and the BID price is the spreads, another fee taken from each transaction the trader makes. The spread is measured in pips.
Pip stands for percentage in point. It is the unit of measurement used to show the amount of change in the exchange rate of a forex pair. The 4th decimal point of the price in your quote is the pip, except for the Japanese Yen.
For example, if the USD/NZD price is quoted at 1.6025, and the price moves to 1.6029, it means the exchange rate has increased by 4pips.
So a forex trader needs to place successful trades to first break-even, then go on to make a profit.
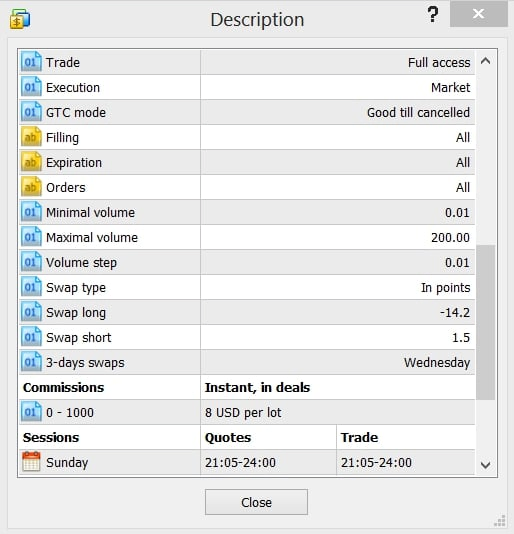
Types of broker commissions
There are two types of commissions and they are both related to the spreads on the currency pair. They’re called:
- Fixed commission
- Relative commission
1. Fixed commission
This commission is charged alongside a fixed spread. No matter the size of the trade or the market conditions at any given time, the fee remains fixed. The brokerage may assign a $2 charge for each transaction, and it doesn’t matter how large the position, the fixed charge will be deducted for every trade you open.
If the brokerage charges a fixed spread between 2 to 3pips, a fixed commission would be attached to this fee.
For example, if the broker quotes the price of the EURUSD at 1.2573/1.2576, then the fixed fee here is three (3) pips. If you place a buy order, and the price moves up to 1.2579/1.2582, the broker would charge the same amount as the fee.
2. Relative commission
This fee is usually based on the size of the trade you make. This type of commission is more common whereby the broker may charge, say a $5 per $10000 traded in volume. So the more you trade, the higher the commission to be paid.
Note that in most cases, a transaction limit is applied for this commission.
For example, the broker may set a limit of $100000 for the $5 fee. This means once you trade $10000 ×10, you would have reached the limit. A new commission fee may be charged for your next trade.
The spread attached to this is charged based on the market conditions and the price moves. It is not fixed. In times of greater liquidity in the market, spreads are often lower. These are times when the currency pair is in high demand and experiences a lot of trading activities.

Trade forex with the best conditions and a regulated broker:
Broker: | Review: | Advantages: | Free account: |
|---|---|---|---|
1. Capital.com  | # Spreads from 0.0 pips # No commissions # Best platform for beginners # No hidden fees # More than 3,000+ markets | Live account from $ 20: (Risk warning: 78.1% of retail CFD accounts lose money) | |
2. RoboForex  | # High leverage up to 1:2000 # Free bonus # ECN accounts # MT4/MT5 # Crypto deposit/withdrawal | Live account from $ 10 (Risk warning: Your capital can be at risk) | |
3. Vantage Markets  | # High leverage up to 1:500 # High liquidity # No requotes # MT4/MT5 # Spreads from 0.0 pips | Live account from $ 200 (Risk warning: Your capital can be at risk) |
Other fees that are charged by forex brokers
Apart from commissions and spreads, brokers may charge other fees, such as:
- Monthly Inactivity fee
- Monthly or quarterly fees
- Margin costs.
Inactivity
This is a fixed sum that brokers charge if a trading account remains inactivity for a specified period. The period and the amount usually depend on the broker. But on average, $10 is charged monthly after three months of inactivity on a trading account.
Monthly or quarterly fees
Some brokers may charge the forex trader a monthly or quarterly account maintenance fee. These fees are usually low and vary.
Margin costs
This is the interest charged when a broker offers you leverage or when you trade on margin. It’s usually a fixed percentage and depends on the broker’s rates.
Some brokers charge other hidden fees, and others may charge for calling the broker after business hours.
Trade from 0.0 pips over 3,000 markets without commissions and professional platforms:
(Risk warning: 78.1% of retail CFD accounts lose money)
Other costs of trading
1. Leverage
Leverage is an opportunity for forex traders to open sizable positions and increase their profit. The broker charges an interest fee for this, and there’s also the risk of the trade going wrong. So forex traders must be cautious when using leverage because it increases their trading costs and risk.
2. Swap fees
Forex traders who leave positions open overnight have to think about the costs. These types of trades attract an interest fee. The fees accumulate the longer the trader leaves the position open.
3. Internet data fees
Forex trading requires the use of internet data. Fundamental analysis through which the trader may understand the market requires information. This information can only be obtained through world economic news. Such news may require news or TV subscriptions that cost money. Forex traders must also factor in these costs when calculating their trading expenses. This would help ascertain if the business is profitable for you or not.

How to reduce forex trading expenses.
Forex trading costs are inevitable, but there are ways to keep your expenses as low as possible. Below, we recommend a few approaches that work in this regard:
1. Use the appropriate commission model for your trading style
A suitable commission model would keep your cost at a reasonable level. First, you need to determine your trading frequency. A fixed commission model may be more appropriate if you’re someone who trades frequently and in high volume. You know what fees to expect, no matter how much you stake on a fixed commission model. Less frequent and low-volume traders should use a relative commission model with a broker whose fees are competitive.
2. Trade at the proper timeframe
Look out for the best time of trade for your currency pair of interest. Liquidity will be high at these times, and it would lead to tighter spreads. So if you’re a trader working with varied commissions and spreads, this would favor you immensely, apart from the other benefits you would enjoy in such a market.
3. Be reasonable and cautious with leverage
As we’ve mentioned, leverage attracts interest fees and increases risk. The forex trader should maintain low leverage in their trading to reduce these fees and risks.
4. Use a suitable trading style
Long-term trading that involves leaving positions open for days or weeks isn’t for everyone. Indeed many people profit from such trading styles, but it requires technical knowledge about market conditions. Before leaving positions open long term, be sure to have ascertained all the costs and the profits that may accrue from that trade. Ensure you have carried out your necessary analysis and are beyond doubt that the currency pair can only yield maximum profits if traded long-term.
Retail forex traders need brokers to trade this financial market. The brokers are in this business to make a profit, and the only way they can do so is by attaching fees and commissions to each service they render. Running your accounts, providing liquidity for your trades, executing your orders, and other services they provide have to attract fees. The forex trader must be aware of these and should compare prices in the market before choosing a broker. It is also crucial to determine your trading style and decide what type of commission model is appropriate and would lessen costs before you proceed. These two factors should guide you in choosing the right broker and the appropriate trading account if you wish to control your trading expenses.
Trade from 0.0 pips over 3,000 markets without commissions and professional platforms:
(Risk warning: 78.1% of retail CFD accounts lose money)
FAQ – The most asked questions about Forex broker commissions :
What is fixed forex broker commission?
Fixed forex broker commission is assessed in addition to a set spread. The cost stays the same regardless of the volume of the trade or the state of the market at any particular time. No matter the position’s size, the brokerage may impose a $3 fee per transaction, which will be deducted from every trade you execute.
What is the relative forex broker commission?
The relative fee is the amount of trade you make typically determines this fee. It is more typical for the broker to charge $2 for every $1000 in volume traded. Therefore, the commission you must pay will increase as you trade more.
What are the additional charges leived by forex brokers apart from commissions?
There are many small to moderate fees or deductions levied on a trader. Brokers charge a fixed amount known as “inactivity fees” if a trading account is inactive for a predetermined time. The length of time and the amount are typically determined by the broker. Some brokers may charge the forex trader a monthly or quarterly account maintenance fee; these costs are often modest and fluctuate.
See more articles about forex trading here:
Forex Broker Ivory Coast
Forex Broker Germany
Forex Broker Poland
Is a Forex broker open on the weekend?
Forex Broker Belarus
Forex Broker Venezuela
Last Updated on January 27, 2023 by Arkady Müller

 (5 / 5)
(5 / 5)