How to trade Futures: Trading tutorial for beginners
Table of Contents
With the number of contracts traded and the size of exchanges growing rapidly, you may be wondering how you can get a piece of the action and make some money. Futures are some of the most popularly traded derivatives for a good reason. The low cost of the contracts and high-profit potential makes them an attractive investment.
But what exactly are Futures? How do they work? And more importantly, what are the things you need to know to make money with futures contracts? If you’ve never traded futures before or need a refresher on the specifics, this guide to futures trading will get you on the right track.

What are Futures?
Futures are derivative financial contracts that bind parties to buy and sell a standardized asset on a specific date or in a particular month for a specific price. Both the buying and the selling party are obligated to transact – regardless of the market price. Since futures are derivatives, their price is determined by the price of another asset. Let’s say you buy stock futures. If the stock goes up, the price of the future will go up. If the stock price falls, the price of the future will fall.
Futures are most commonly traded with commodities like crude oil, gold, or coffee. If someone gets their hands on a coffee future, they agree that they will buy 37,500 pounds of coffee from the seller at the agreed-upon date for a specified price. Unless the buyer or the seller decides to trade the contract with another buyer or seller, they must complete the transaction on the stipulated date. Futures trading isn’t limited to commodities. You can buy stock futures, forex futures, index futures, and a variety of other futures. But regardless of the underlying asset, both parties must transact at the end of the contract’s term.
Note:
Futures are mainly used for hedging and speculation but it was invented for the economy to determine fixed prices for a business transaction in the future.
The contracts can hedge or limit the losses caused by an asset’s price movement. With a futures contract, a trader can also speculate on the price movement of any financial instrument.
How Futures work:
The concept of futures was born when traders had the idea of “locking in” the prices of commodities. For futures to work, traders must play two roles – the hedger and the speculator. The hedgers are those that want their business to be stable and predictable. Let’s say you’re a coffee farmer, and you’re concerned that the price of coffee will fall six months down the line. The price decline will lead to a decrease in the profit margin or even significant losses.
In this scenario, you can lock in the price of your coffee by selling short futures contracts that expire in six months. “Selling short” means that you’re betting that the prices will decline. If the price falls as you had expected, while your business will suffer, the decrease in profit margins will be offset by the futures contracts.
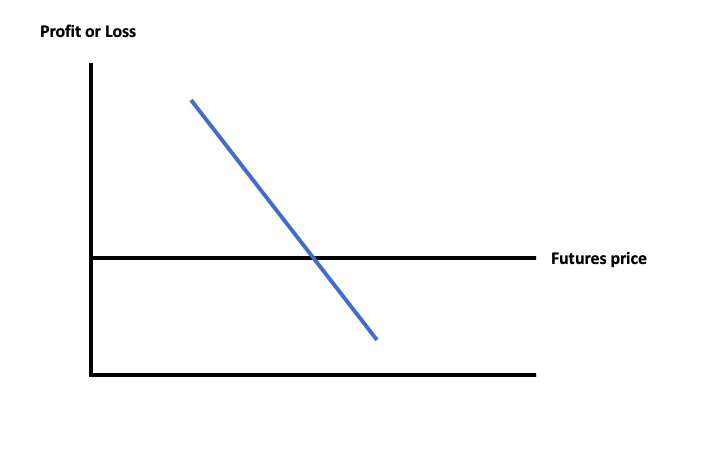
Now let’s assume there’s a company that buys coffee, packages it, and sells it. But this company is concerned that the price of coffee will rise, affecting the bottom line. This company can also use a futures contract to “lock-in” the price, so the potential losses are offset.
Both the company and the farmer are hedgers – they don’t trade futures for making a profit. They only trade them to ensure business stability and prevent losses. On the other hand, speculators trade for profit, and futures appeal to them because of the rapid price movements, high liquidity, and low margins. Also, unlike hedgers, speculators close their contracts much before expiration.
Note:
The underlying product does not matter to the speculator – they are only interested in the profits.
Futures Contract specifications:
Contract specifications are the key components of futures contracts. These include:
- Contract size: The contract size represents the quantity of assets being bought and sold in the contract. It is standardized and does not change, but the quantities traded are different for every asset. For instance, a crude oil contract has a size of 1000 barrels, and a corn contract has a size of 5000 bushels.
- Contract value: Contract size multiplied by the current price of the asset represents the contract value. If a bushel of corn is trading for $4, the contract value will be $4 x 5000 = $20,000.
- Tick size: The tick size defines the minimum price by which a contract can fluctuate. Most contracts have tick sizes quoted in dollars and cents, but some contracts define the tick size in fractions of a penny.
- Delivery: A futures contract can either be cash-settled or physically settled. The difference between them is easy to understand. A cash-settled contract will expire into cash, and a physically-settled contract will expire into the physical commodity.
- If a contract is physically settled, the details of the delivery are included in the contract.
Differences between Futures and Options trading
With an options contract, the holder isn’t obligated to buy or sell anything. They only have the right to do so. On the other hand, both the buyer and seller are obligated to transact with a futures contract.
Additionally, when trading futures, you will need to balance your accounts at the end of every trading day. Traders don’t need to do this when trading options.
While balancing your accounts every day may seem like an inconvenience, you need to do it since the market may move in a way that you need to add funds to your account every day until the contract is complete. For more information, you can read our Options vs. Futures article.
History of Futures
Futures have a long-standing history in trading. Some of the earliest futures contracts come from the earliest recognized futures trading exchange in Japan – the Dojima Rice Exchange. Established in 1730, the exchange facilitated the trading of rice futures.

While the western concept of commodity futures was first introduced in England in the 16th century, the country’s first commodity exchange, the London Metals, and Market Exchange was not established till 1877. The earliest official trading exchange in the west, the Chicago Board of Trade, was established in the United States in 1848. The exchange was founded after railroads and telegraph lines connected agricultural hubs of Chicago with hubs in other cities.
Only corn futures were traded initially, with the trade of wheat and soybean futures ramping up soon after. In 2007, the CBOT merged with the Chicago Mercantile Exchange. But to date, these three commodities account for the bulk of the trading conducted at the exchange. A few years later, in 1870, the New York Cotton Exchange was established, and over time, more and more futures contracts were developed for other products.
It wasn’t until the 1970s, a hundred years later, that futures trading markets saw significant growth. During this period, exchanges began allowing futures trading in foreign currencies and also in various financial futures. While there are futures trading exchanges worldwide, U.S. exchanges are by far the most widely traded.
Why should you trade Futures?
Futures offer several benefits that other instruments don’t offer, which is what gives them a unique appeal. Some of the benefits trading futures offers include:

Risk mitigation:
Regardless of whether you’re investing in a single stock or a portfolio of stocks, you can limit risk to your investment using futures. If you own a single stock, you can hedge risks by selling your futures at a higher price than which you bought the shares. But bear in mind that the number of futures you sell should be equal to the number of shares you own. If prices fall, the selling order will offset your equity losses and vice versa. In this way, you’re guaranteed a return, and market fluctuations won’t affect your portfolio as much.
Leverage:
If you buy stocks, you will need to pay the full price of the shares. However, if you buy futures, you don’t need to pay in full. You must only pay a percentage of the value of the shares, called the margin. Since you’re paying less for the same amount of shares, with futures, you can spend less money and own more shares than you would if you would buy stock with your capital. While leverage can multiply your profits, it can also multiply your losses.
Lower cost:
Getting involved in the stock market demands a lot of capital. But the futures market does not. Furthermore, you don’t have to maintain a futures account – as long as you have enough in it to cover the margin. The margin ranges between 3% and 9% of the contract value.
Prices move with underlying assets:
With options, the underlying asset’s price may shift, but the option’s price may remain at a standstill. But this is not the case with futures. If the price of the asset moves, the price of the futures contract will move with it. So, you can use technical analysis techniques right on the futures market without worrying about derivative pricing.
No short-selling restrictions:
Unlike the stock market, there are no restrictions on long and short positions in the futures market. This allows you to stay impartial between long and short positions and trade according to your market analysis without worrying about financial regulations.
Dependable volume data:
If you were trading in the forex market, you would find it next to impossible to get your hands on reliable volume data. But you won’t have those problems with futures contracts. With the accurate data at hand, you can tell which players are interested in trading and carry out unambiguous technical analysis.
Disadvantages of trading Futures
Like everything, futures trading isn’t without its drawbacks. The disadvantages you need to vary about include:

- Higher commissions: Futures markets make it extremely easy for traders to overtrade. If you make too many marginal trades, you will need to pay a lot of commissions. Even though you may have made some great trades, there’s always a chance you will have spent a lot to make it happen. Having a solid money management strategy is a must if you want to get involved in futures trading.
- High pressure: The low capital requirements of futures trading put most traders in the “I cannot afford to lose” mindset. The pressure can lead to making some simple yet expensive mistakes, pushing you out of the market.
Futures Order Types
Some of the most used order types include:
- Market order: With market orders, you can buy or sell futures immediately. While this order guarantees that your order will be filled, it does not guarantee the execution price. Timing it badly will lead to losses.
- Stop order: It is an instruction to buy or sell your futures when the price climbs or falls to a specific point – the stop price.
- Limit order: These enable you to buy or sell your futures at a specific price or better. Limit orders are of two types: buy limit orders and sell limit orders. A buy limit order will be executed either at the limit price or lower. On the other hand, the sell limit order will be completed at either the limit price or higher.
- Day order: The day order expires at the end of the trading if the trade has not been executed by then.
- Market-on-Close (MOC) orders: These are similar today orders. The futures will be bought or sold at the closing price of the trading session. These orders are typically used by traders that don’t want to hold a position overnight.
- Good Til’ Canceled (GTC) orders: These orders remain active until executed or canceled.
Terminology you need to know before future trading
Margin has a different meaning in stock and futures markets. In the stock market, buying on margin means that you’re borrowing money from a broker to buy stocks. In this scenario, the trader is effectively taking a loan from the brokerage to buy more stock than they usually can.
However, when trading futures, the trader must put down a sum of money as a good-faith deposit. This sum of money is called the margin. The margin you pay is legally considered a performance bond, ensuring that both the buyer and the seller meet their obligations when the time comes. The initial margin requirement is rarely the same. The price you must pay varies by product, and market volatility also plays a significant role in it.
The exchange holds the sum of money you pay, and if the prices move against your position, a margin call is produced, requiring you to wire more funds into your account.
Note:
If a trader does not supply the funds in time, the futures contract may be liquidated.
Additionally, you need to know these two terminologies:
- First Notice Day: The First Notice Day is when a notice of intent to deliver the underlying commodity is sent to the trader. Most investors close their positions before the First Notice Day since they don’t wish to possess the commodity physically.
- Last Trading Day: The Last Trading Day is the final day before the cash settlement or the delivery of the underlying asset.
How to trade Futures:
There is no shortage of trading platforms, tools, and resources, and trading futures has never been this easy. Here are some things you need to know before you start trading futures:
Minimum capital requirements
Futures markets are some of the most accessible trading markets since you don’t need as much capital as you need to trade stocks. But bear in mind that you will need to invest a lot more to trade futures than you would to trade in forex markets. There is no minimum capital requirement from a legal standpoint, and different brokers set different minimum deposits.
Also, the margin you must pay for the same commodity may vary from broker to broker. In general, though, E-mini futures have the lowest trading margins, and you may be able to trade them with as little as $500 in your trading account.
Finding the right broker
If you’ve never traded futures before, finding the right broker to do business with can seem complicated. Make sure you consider the following factors when deciding if a broker is right for you:
- Trading fees: If you trade a lot, the commissions you need to pay will stack up quickly. When deciding whether a broker is right for you, ensure that the brokerage has a transparent fee structure and offers competitive fees. Go through the fine print and find if the brokerage charges any additional fees and penalties.
- Platform: The trading platform must be easy to navigate and offer charts and analysis tools that help you make smarter trading decisions. Always check whether the broker requires you to pay extra for some features. Also, ensure that the platform boasts fast execution speeds.
- Support: A lot of trades you make will be time-critical. The brokerage must have an active customer support team that you can rely on. Top brokerages offer 24/7 support over live chat and phone calls and allow traders to open a ticket via email.
Strategizing and selecting the right Future
After signing up for the broker and making a deposit, you need to select the right futures contract. Your first step should be selecting a market you know a lot about. Then, you can apply strategies depending on the circumstance and hope that things go your way, so you turn a profit.
You must apply fundamental analysis since looking at charts and understanding patterns will help you speculate price movements. After your initial analysis, you must consider some factors that will impact your instrument’s performance. Some of these factors you must consider when choosing a future to invest in include:
Movement
Some instruments like crude oil are incredibly volatile. Before you invest any capital, you must take into account the asset’s price movements. Understanding the price movement is easy – all you have to do is look at the asset’s point value and estimate how much it could move by looking at the movement history.
With an easy average true range calculation, you will know how volatile the asset you’re interested in is and decide if you want to enter a position. Finding the range is easy in and of itself. You only need to calculate the difference between the highest and lowest price of the asset. However, finding the true range is a little more complicated. This is because futures often have price gaps almost daily. To calculate the true range, you must find the true high and subtract the true low from it.
The true high is the highest point the asset has touched today, or yesterday’s closing point, whichever is higher. Likewise, the true low is the lowest point the asset has touched today, or yesterday’s closing point, whichever is lower. Let’s say an asset closes at 99 points one day, opens at 100 the next day, and reaches a high of 101. The range would be 101 – 99. With this value, you now have an indicator of the asset’s volatility and can factor it into your trading decision.
Volume
The volume of the contract is the number of times it is traded in a single day. We recommend that you only trade contracts that have a volume of over 300,000. A high volume indicates that you’ll always have someone to buy from or sell to in the market. 10-year treasury notes, crude oil, and E-mini contracts are some of the most heavily traded contracts.
After you analyze the movement of the asset, you must consider the margin you need to pay. Some futures, such as crude oil futures, demand you to pay high margins, while others aren’t as expensive to get your hands on.
Best Futures for beginners to trade
Now that you understand what you should look for before getting a futures contract, which asset’s futures should you opt for? If you’re low on capital, getting E-mini S&P 500 futures is the right way to start your trading journey. The margins are sometimes as low as $500, and since they’re traded heavily, you don’t have to worry about being stuck with a position.
Take a look at the S&P 500 Futures chart:
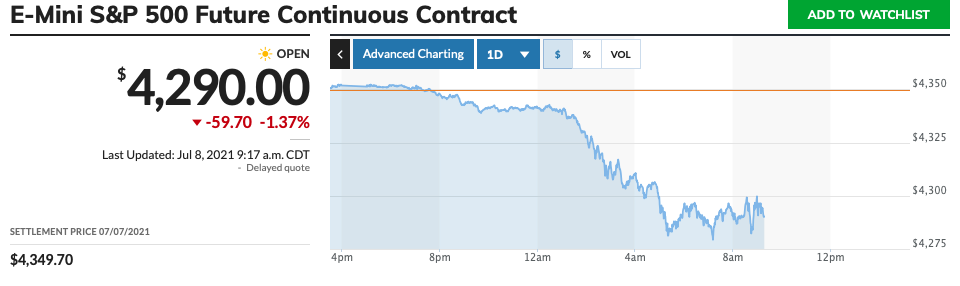
10-year treasury notes are also a great choice, but bear in mind that they aren’t traded as much as E-mini futures. These aren’t as volatile, but the price movement is decent, and you will get a clear picture of the market by looking at a one-minute chart. Finally, trading crude oil futures is also a good idea for some beginners. Of the three recommendations, crude oil demands the highest margin. However, the asset is the most volatile, giving you more opportunities for profit (and loss).
The best Future trading strategies
There are dozens of excellent futures trading strategies that you can employ and make money. Some of the simplest ones have been highlighted below:
- Day Trading: In this strategy, you enter and exit futures positions on the same day.
- Spread Trading: A spread trade involves the simultaneous purchase and sale of related futures contracts.
- Momentum Trading: You must first find a narrow trading channel or range where there is no volatility. You can then wait for the price to break out of the channel with a concurrent spike in open interest. The surge in volatility enables you to catch a strong trend and make money.
- Position Trading: The strategy involves holding a position for a long period – typically days or months.
- Options on Futures: You could buy an option that gives you the opportunity but does not obligate you to execute a trade on an underlying futures contract.
- Scalping: The idea is to limit your losses to a maximum of two ticks and cash in on profit as soon as you see you’ve got it. The strategy can be coupled with spread trading, enabling you to gain profits quickly.
You can always put your own spin on these strategies if you find that personalizing them yields better results. A good strategy will keep the trader in check and remind them of the risk. The key to success is to find the strategy that compliments your trading style. As long as you don’t try to get huge yields from smaller trades, any of these strategies may bring you great results.
Futures trading: Top tips
Applying just one strategy could make you a profit, but if you want to make money trading futures consistently, you will need to bear many factors in mind. Investing time and money into finding the right broker is one of the best things you can do to increase your chances of success. Next, you must test out the best strategies since those give you the best chances of making money.

Learning to trade is a continual process – you won’t get better at it in a day. To help you learn and grow faster, here are some top futures trading tips:
- Practice first, bet later: Regardless of what type of futures you’re trading, practicing trading the future using a demo account is the right way to go. Once you’re familiar with the market and know what strategy works, you will be much more confident, and the probability of making profits will also be higher. Demo accounts come funded with play money, removing all the risk from participating in the market.
- Use a strategy: Struggling with disciple is a lot more common than you’d think. Emotions like greed and fear will disrupt your ability to make sensible trading decisions, which is why you must always have a strategy to stick to. Your mind may distract you, but numbers never lie.
- Don’t pay high margins: Paying larger margins may enable you to make more money. However, only getting involved with futures that have high margins isn’t a good idea. A sensible trader keeps risk and margins low, so they can keep trading for longer and not lose all of their capital.
- The news is your friend: An asset may experience a sudden rise or fall in price after an announcement. Make sure you’re always in the loop and keep your eyes open for news reports that may affect your positions. Business Insider, Bloomberg, Yahoo! Finance, and CNBC are some of the best trading news sites.
But perhaps the best tip we could give you is to educate yourself about trading and the various markets continually. Luckily, there is no shortage of resources you could use to become a better trader.
Some of the most valuable resources for traders include:
- Books: These are undoubtedly the top learning resource for traders. You can learn strategies in detail, get insight into how the best traders work, and learn from their stories.
- Courses: You can find free trading courses on YouTube, and if you don’t mind investing in yourself, you can buy courses from sites like Udemy to learn how to trade. These courses also teach you how to make trading signals and how to use indicators to find patterns.
- Blogs: Several blogs on the internet regularly post about market trends. Reading blog posts can help you get more perspective on your trades.
- Chat rooms: Trading chat rooms are an excellent place to interact with other traders, learn their strategies and ask them questions. Most market updates are discussed in chat rooms, and they can be a fantastic source of information. If you haven’t joined any chatroom before, joining Warrior Trading or BuySide Global rooms is an excellent idea.
- Free eBooks: A lot of free PDFs can help you understand trading better. Some also include the best chart setups and impart you with the best strategies for futures trading.
Conclusion: Futures trading has high potentials
Trading futures can be complicated. However, with this guide, you are now one step closer to making money with them. Your next move should be learning and practicing strategies with demo accounts. The more you practice, the faster you can move on to investing real capital.
FAQ – The most asked questions about Futures :
What is the meaning of Futures?
Futures are types of contracts in which the holder has the right to acquire or sell his particular asset at a speculated price and on the speculated date set by them in the future. For trading such contracts, you need to have an approved brokerage account through which you can carry out your futures exchanges.
What are the best Futures for beginners to trade with?
For beginners, you should preferably go with E-mini S&P 500 if you seem to be low on funds, as it is the correct path to walk for your trading journey. You can seem to observe the margins going as low as 500 dollars. These futures are traded in huge bulk amounts, and thus you need not worry about lingering in a particular position for too long.
You can also opt for 10-year treasury notes, but you should know that they are not traded in the same amount as E-mini futures. They experience a decent price movement without being too much volatile, and you can clearly understand the position of the market with just a chart of one minute.
What are the top Futures?
With a well-designed plan for trading and enough funds in hand, you can select the right futures for trading and become rich in a short time. Currently, the top five futures to trade are crude oil, natural gas, gold, soybeans, and corn.
See our other blog articles:
Last Updated on January 27, 2023 by Arkady Müller

